What is the difference between Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion?
Defining Uniform Motion
Uniform motion is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the motion of an object travelling equal distances in equal intervals of time, regardless of the duration of those intervals. In simpler terms, if an object moves with uniform motion, it maintains a constant speed throughout its journey. This means that the object does not accelerate or decelerate, resulting in a consistent rate of travel.
Formula:
\[
\text{Speed (v)} = \frac{\text{Distance (d)}}{\text{Time (t)}}
\]
For example, consider a vehicle cruising on a highway at a steady speed of 60 kilometres per hour. If this vehicle continues to travel at that speed, it will cover 60 kilometres in one hour, 120 kilometres in two hours, and so forth. Each time interval is equal, and the distance travelled during each interval remains constant, exemplifying uniform motion. This consistency in distance and time illustrates the key characteristic of this type of motion.
Uniform motion can be visually represented on a graph, where the distance is plotted against time. In such a graph, the resulting line will be straight and diagonal, indicating that for every increment in time, there is a corresponding equal increment in distance.
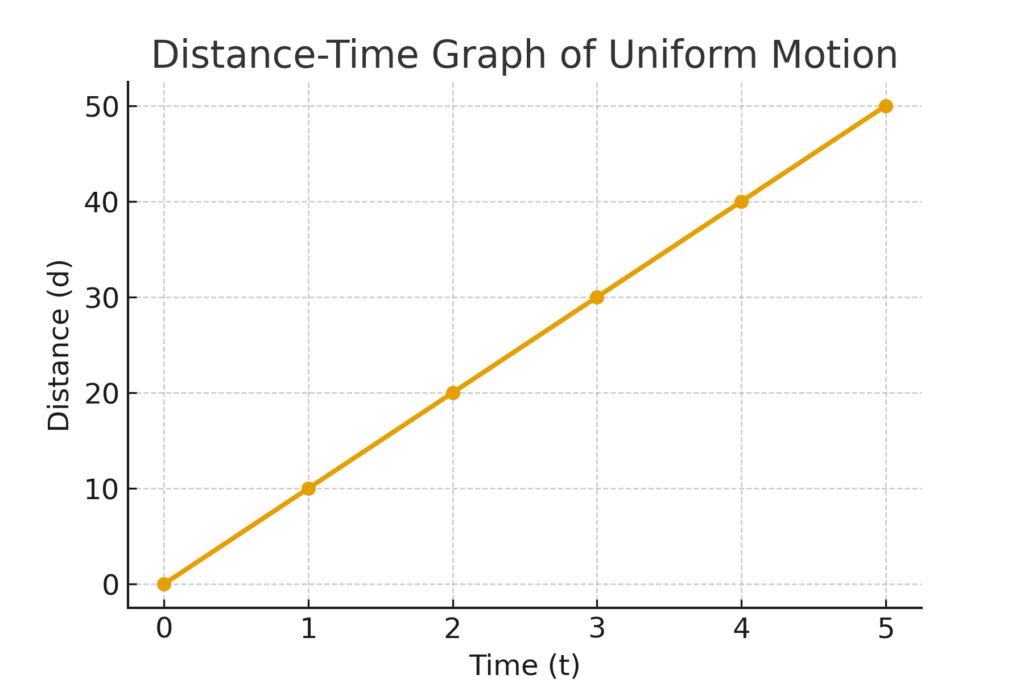
Such graphical representations further emphasise the relationship between distance, time, and the steady pace characteristic of uniform motion.
It is important to distinguish uniform motion from other forms of motion. For instance, in non-uniform motion, an object’s speed may vary, leading to unequal distances being covered in equal time intervals. Therefore, a clear understanding of uniform motion is essential for grasping more complex concepts in physics, such as acceleration and variable speed. By recognising this fundamental behaviour, one can better appreciate the dynamics of movement in various real-world scenarios.
Characteristics of Uniform Motion
Uniform motion is characterised by certain defining features that set it apart from other types of motion, particularly accelerated motion. One of the primary attributes of uniform motion is the consistency of speed. In this type of motion, an object travels at a constant rate, meaning that the distance covered in equal time intervals remains unchanged. This constancy ensures that uniform motion is predictable and easily quantifiable, distinguishing it from motion where speed varies over time.
Another critical aspect of uniform motion is its trajectory. Objects in uniform motion follow a straight-line path. This linear trajectory is crucial because it implies no deviations or changes in direction; consequently, the analysis of uniform motion remains straightforward, focusing solely on speed and distance. This contrasts sharply with accelerated motion, where an object may change direction or speed, resulting in a more complex analysis that takes into account varying rates of acceleration and angular displacement.
Additionally, uniform motion is characterised by the absence of acceleration. In this context, acceleration refers to any change in velocity, encompassing both changes in speed and direction. In uniform motion, since the speed is constant and the object does not veer off its straight path, the acceleration is effectively zero. This null acceleration further reinforces the simplicity of uniform motion, allowing for the application of basic kinematic equations without the complication of variable acceleration.
Understanding these characteristics—constant speed, straight-line trajectory, and lack of acceleration—is crucial for differentiating uniform motion from other types. The knowledge of how uniform motion operates not only aids in the comprehension of fundamental physics concepts but also serves as a foundation for exploring more complex scenarios involving motion.

Butterfly Edufields 100+ Motor Machines Kit
Science Experiment Kit |
Toys for Boys 5 6 7 8 9 10 Year Old |
Birthday Gift for Boys Girls Age 6-10 8-10 |
DIY STEM Projects Kit
Click To Buy on Amazon
Real-Life Examples of Uniform Motion
Uniform motion can be observed in numerous real-life scenarios, making it easier to understand this fundamental concept of physics. One of the most relatable examples of uniform motion is a train travelling along a straight track at a constant speed. In this case, the train maintains a steady velocity, which means it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time without changing its speed or direction. The smooth and predictable journey of the train illustrates how an object in uniform motion behaves, providing a practical context for this theoretical concept.
Another prime example of uniform motion is a car cruising along a highway at a constant speed. When a driver sets the cruise control feature, the vehicle adjusts to maintain a designated speed, ensuring that it travels equal distances within consistent time frames. This application of uniform motion enables drivers to conserve fuel and maintain a relaxed driving experience, demonstrating the prevalence of this type of motion in everyday life. Motorists can easily grasp the importance of uniform motion as they navigate through traffic and strive to adhere to posted speed limits.
In the domain of light phenomena, consider a beam of light spreading in a vacuum. The speed of light in a vacuum is constant, approximately 299,792 kilometres per second (or approximately 186,282 miles per second). This consistent speed means that light maintains uniform motion, travelling vast distances in a straight line without changing its velocity. Consequently, the behaviour of light aids in understanding concepts such as optical properties, communication technology, and even astronomical observations.
These relatable examples illustrate the concept of uniform motion effectively. By recognising how uniform motion manifests in trains, cars, and light, readers can better appreciate the theory while drawing connections to their own experiences, thereby enhancing their understanding of this essential physical principle.
Applications and Implications of Uniform Motion
Uniform motion, characterised by movement at a constant speed in a straight line, has critical applications across various fields, significantly influencing both theoretical and practical aspects of life. In physics, uniform motion serves as a fundamental concept that aids in understanding kinematics and dynamics. It forms the basis for developing equations that describe the motion of objects, allowing scientists and engineers to predict behaviours in various scenarios. This predictability is vital in fields where precise calculations are necessary, such as aerospace and automotive engineering.
In the engineering domain, the principles of uniform motion are essential for designing effective transportation systems. Engineers utilise uniform motion concepts when calculating travel times and designing roadways or railways to ensure efficiency and safety. The design of high-speed trains and aircraft relies heavily on uniform motion principles, as understanding constant velocity allows for optimising routes and enhancing fuel efficiency. This consideration has profound implications in developing sustainable transportation solutions capable of minimising resource consumption and environmental impact, thereby contributing positively to societal advancement.
Beyond the realms of science and engineering, uniform motion also plays a vital role in sports performance analysis. Coaches and athletes employ techniques based on uniform motion to enhance training regimens and improve performance metrics. By analysing the trajectories and velocities of athletes during uniform motion periods, they can determine optimal techniques and tactics, leading to better results in competitive settings. Furthermore, understanding uniform motion is essential in grasping natural phenomena, such as the motion of celestial bodies and projectiles. It fosters a deeper appreciation for the laws of nature, bridging the gap between theoretical principles and real-world experiences.
Key Difference: Uniform vs. Non-Uniform Motion
- Uniform Motion: Constant speed, equal distance in equal time, zero acceleration.
- Non-Uniform Motion: Speed varies, distances are unequal in equal times, and involve acceleration or deceleration.
FAQs on Uniform Motion
Q1. What is uniform motion in simple words?
Uniform motion means moving at a constant speed in a straight line without speeding up or slowing down.
Q2. Give two real-life examples of uniform motion.
A train moving at a constant speed on a straight track, and a car on cruise control.
Q3. What is the formula for uniform motion?
\[
v = \frac{d}{t}
\]
where v = speed, d = distance, t = time.
Q4. What is the difference between uniform and non-uniform motion?
- Uniform Motion: Equal distance in equal time, constant speed, zero acceleration.
- Non-Uniform Motion: Unequal distance in equal time, variable speed, involves acceleration or deceleration.
In conclusion, uniform motion is not merely a theoretical concept but a crucial framework that influences various aspects of our daily lives, enriching our understanding and optimising applications across diverse fields.
